Navigating the world of financial protection and guarantees can often feel daunting, especially when it comes to understanding specialized forms such as insurance bonds. Yet, whether you’re an individual, a business owner, or even an event organizer, it’s crucial to grasp what insurance bonds are, how they work, and most importantly, who these bonds are for.
In this blog post, we’ll demystify insurance bonds, highlighting their importance and benefits, and guide you through scenarios where it might be necessary. As your trusted advisor, Torian Insurance aims to provide you with valuable insights and personalized solutions to meet your unique business needs. So, let’s dive in and untangle the complexities of insurance bonds together.
Understanding Insurance Bonds
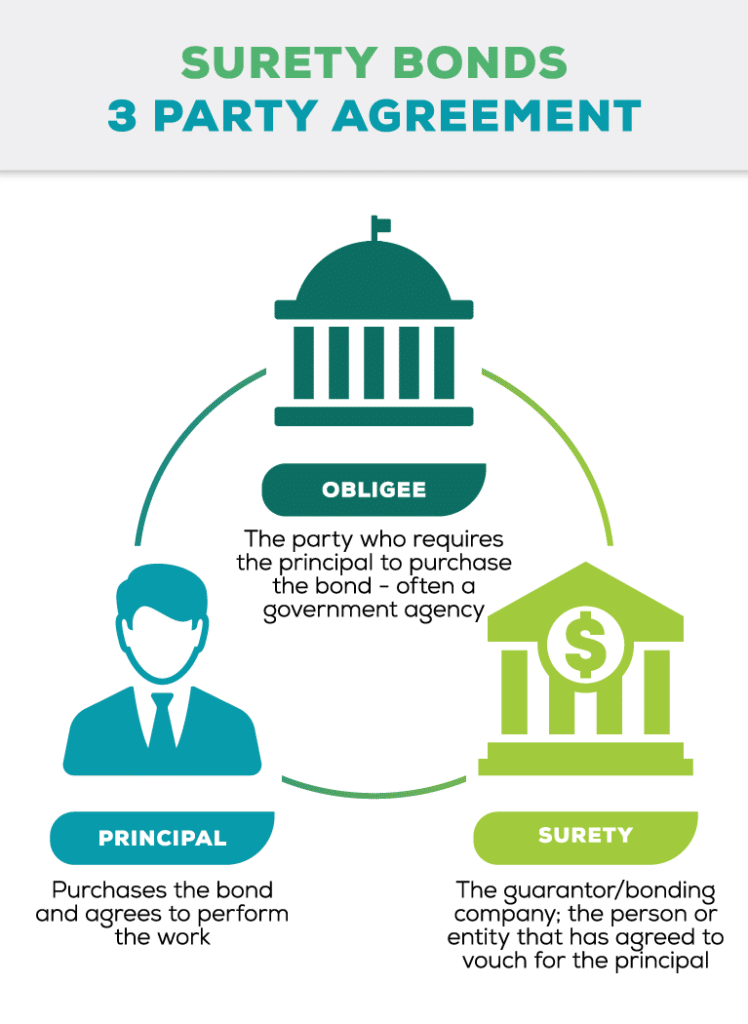
Insurance bonds, also known as surety bonds or fidelity bonds, are technically not a type of insurance. Rather, it is a financial product that provides a guarantee to bondholders in case of default by the bond issuer. It is a safety net that ensures investors are not left at a loss if the bond issuer is unable to meet their financial obligations.
A bond is a contractual agreement involving three parties: the principal (the individual or company responsible for obtaining the bond and performing the work), the obligee (the person or entity requiring the bond), and the surety (the guarantee of the bond). The bond guarantees that the principal will fulfill their contractual obligations. If the principal fails to do so, the surety will compensate the obligee for damages up to the bond’s amount. In essence, an insurance bond protects the obligee from losses from financial harm if the principal does not meet their responsibilities.
How Insurance Bonds Work
To understand how an insurance bond works, consider the following scenario of a surety bond. Let’s say a construction company, ABC Builders, is awarded a contract to build a new office building for XYZ Corporation. As part of the contract requirements, XYZ Corporation requires ABC Builders to obtain a surety bond to ensure that the project will be completed as agreed. In this scenario:
- The Principal: ABC Builders is the principal in the surety bond agreement. They are the ones undertaking the construction work and are responsible for completing the project according to the terms of the contract.
- The Obligee: XYZ Corporation is the obligee in the surety bond agreement. They are the entity that requires ABC Builders to obtain a surety bond. The obligee wants assurance that the construction project will be completed as promised and that they will be compensated if ABC Builders fails to fulfill their obligations.
- The Surety: In this case, the surety is a surety bond company that provides the bond to ABC Builders. The surety company evaluates the financial stability and capability of ABC Builders to complete the project. If ABC Builders defaults on the contract, the surety company will step in to provide compensation to XYZ Corporation up to the bond amount.
So, if ABC Builders fails to complete the construction project as agreed, and XYZ Corporation suffers financial losses as a result, they can file a claim against the surety bond. The surety company will then investigate the claim and if deemed valid, they will compensate XYZ Corporation for the damages incurred, up to the predetermined bond amount. The surety company will then seek reimbursement from ABC Builders for the amount paid out.
In this example, the surety bond acts as a form of protection for XYZ Corporation, ensuring that they are financially protected in the event that ABC Builders does not fulfill their contractual obligations. It also provides assurance to XYZ Corporation that the construction project will be completed as agreed, as the surety company has conducted due diligence on ABC Builders before issuing the bond.
Importance and Benefits of Insurance Bonds
Insurance bonds play a vital role in the financial world. For instance, in the construction industry, it’s often required to win bids for construction projects, which protects the owner of the project from potential losses. Furthermore, some government agencies or landlords require a bond to proceed with the project to protect them in case obligations are not followed through.
This robust protection can significantly lower the level of risk associated with investing in bonds that the principals in these scenarios are undertaking.
Breaking Down The Different Types of Bonds


Insurance bonds can be broken down into two primary types: surety bonds and fidelity bonds. The main difference is a surety bond guarantees the performance of a specific obligation, while a fidelity bond provides coverage for losses resulting from dishonest acts by individuals.
Surety Bonds
As previously mentioned, surety bonds are a type of insurance bond that involves a contractual agreement between three parties: the principal (the party that purchases the bond), the obligee (the party that requires the bond), and the surety (the company providing the bond).
Surety bonds are commonly used in construction projects, government contracts, and various business transactions to ensure that the principal fulfills their contractual obligations. There are two main categories of surety bonds: commercial bonds and contract bonds.
Contract Surety Bonds
Contract bonds, also known as contract surety bonds, are a type of surety bond specifically designed for contractor projects to ensure that the contractor fulfills their obligations as outlined in the agreement.
These bonds serve as a guarantee that the contractors, subcontractors, or suppliers will complete the project according to specified terms, including meeting deadlines, staying within budget constraints, and adhering to quality standards. Contract bonds are commonly required for public projects, such as construction of infrastructure or government buildings, and are often necessary for private projects as well.
Contract bonds provide protection for project owners, investors, and subcontractors by ensuring that the contracted work is completed as agreed upon. Examples of contract surety bonds include:
- Bid bonds– a type of surety bond that contractors provide as part of the bidding process for construction projects. They guarantee that the contractor will enter into a contract if awarded the project and will provide a performance bond.
- Performance bonds– ensure that contractors fulfill their contractual obligations and complete a project according to the terms of the agreement. They provide financial protection to the project owner in case the contractor fails to meet the requirements.
- Payment bonds– guarantee that contractors will pay subcontractors, suppliers, and laborers involved in the project. They protect these parties from non-payment by the contractor and ensure that all financial obligations are met.
Commercial Surety Bonds
Commercial bonds, also known as license and permit bonds, are essential for ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations in various industries. These bonds serve as a guarantee that businesses will conduct their operations ethically and in accordance with legal requirements.
In the event of a breach of the bond terms, stakeholders, customers, or the public can file a claim to seek compensation for any damages incurred. These bonds provide financial protection and uphold the integrity of business practices within specific sectors. Examples of commercial surety bonds include:
- License bonds– a type of commercial bond that certain businesses or professionals are required to obtain as a condition of getting licensed. These bonds serve as a guarantee that the licensee will comply with laws and regulations related to their industry or profession.
- Permit bonds– bonds that contractors or individuals may need to obtain before obtaining a permit for specific projects, such as construction or renovation. These bonds provide protection to the issuing authority in case the permit holder fails to comply with the terms of the permit or applicable regulations.
Surety bonds are an essential risk management tool for businesses and individuals to secure contracts, comply with regulations, and protect against financial losses due to non-performance.
Fidelity Bonds
Fidelity bonds, also known as dishonesty bonds or employee dishonesty bonds, provide coverage for losses resulting from dishonest acts such as theft, fraud, or embezzlement committed by employees. Fidelity bonds protect businesses from financial harm caused by employee misconduct and provide reimbursement for losses suffered as a result of dishonest acts.
These bonds are commonly used by businesses of all sizes to safeguard their assets, protect against internal theft or fraud, and provide peace of mind to customers, stakeholders, and business partners. Fidelity bonds supplement internal controls, background checks, and other risk management measures to mitigate the risks associated with employee dishonesty and safeguard the financial integrity of a business.
Who Needs Bonds and Why?
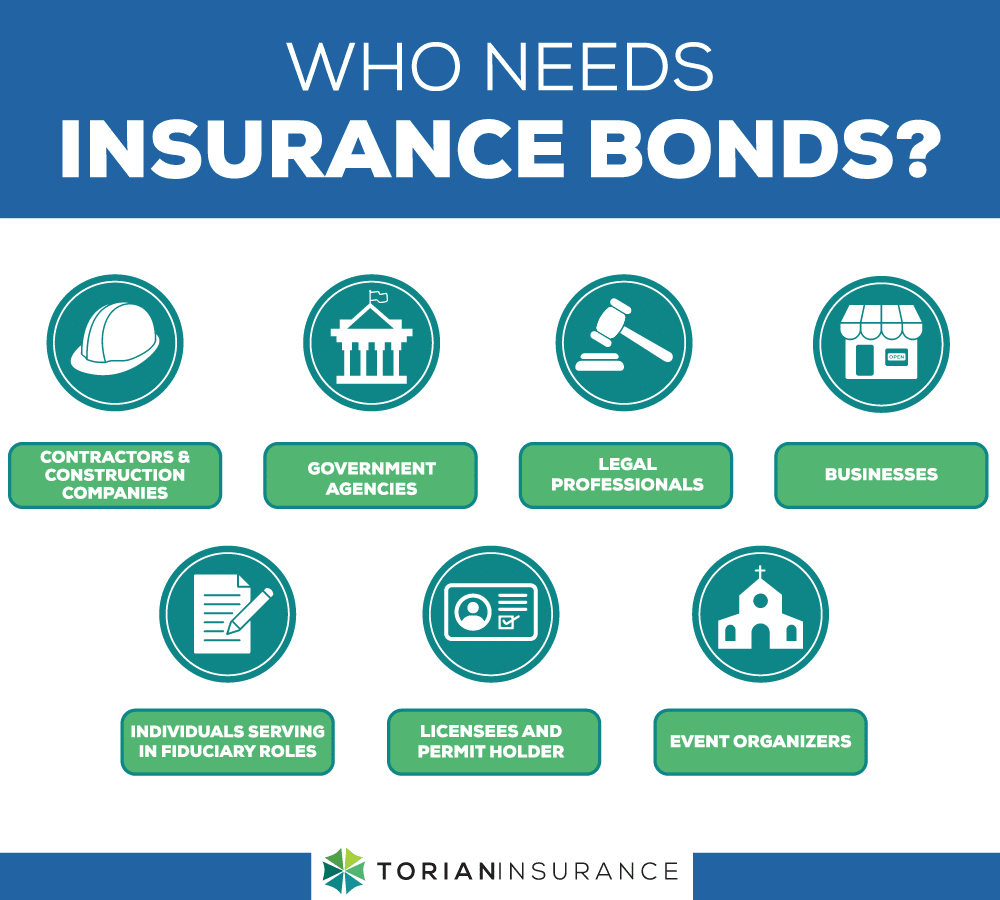

An insurance bond isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution, but rather, it holds significance for a specific set of individuals, businesses, and scenarios. At the forefront are investors, particularly those investing in municipal bonds. These investors rely on insurance bonds to safeguard their investments, especially in situations where the bond issuer might default.
- Contractors and Construction Companies: Contractors often need insurance bonds, such as bid bonds, performance bonds, and payment bonds, as a requirement in the bidding process for construction projects. These bonds provide financial protection to project owners, ensure contractual obligations are met, and guarantee payments to subcontractors and suppliers.
- Government Agencies: Government agencies often require insurance bonds from contractors and vendors to ensure compliance with regulations, protect public funds, and guarantee the completion of projects or services as contracted.
- Legal Professionals: Notaries public and legal professionals may need notary bonds and court bonds to provide financial security and ensure compliance with legal requirements during the execution of legal documents and court proceedings.
- Businesses: Businesses may obtain fidelity bonds to protect against employee theft, fraud, or dishonesty. They can also purchase insurance bonds as part of surety agreements or for licensing requirements in specific industries.
- Individuals Serving in Fiduciary Roles: Individuals serving as administrators, executors, trustees, or guardians may need fiduciary bonds to guarantee the proper administration of estates or trusts, protect beneficiaries, and comply with legal obligations. ERISA bonds are often required in an amount equal to 10% of the value of employee benefit plans, 401K’s, etc.
- Licensees and Permit Holders: Many states and municipalities require licensees, including contractors, auto dealers, and other professionals, to obtain license bonds as a condition of receiving and maintaining their licenses. Permit holders may also need permit bonds to ensure compliance with building codes and regulations.
- Event Organizers: Event organizers often need insurance bonds, such as permit bonds or special event cancellation insurance, to protect against unexpected events that may disrupt or cancel an event. These bonds provide financial security in case of non-performance by vendors, failure to meet contractual obligations, or unforeseen circumstances that lead to event cancellation.
Insurance Bond Needs in the Tri-State Area
The tri-state area is home to a diverse range of industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, construction, and service businesses. These sectors often require insurance bonds to guarantee the fulfillment of large contracts and to protect against financial loss.
For instance, agricultural companies might need an insurance bond due to the unpredictability of crop yields and weather conditions, while manufacturing firms could use it to ensure contractual obligations are met.
Moreover, the tri-state area is a hub for numerous events and entertainment activities. From sporting events to music festivals, these occasions often need insurance bonds to safeguard against cancellations, non-performance, or financial default. The local government in the tri-state area may also require insurance bonds for public works projects to ensure taxpayers’ money is well-protected.
Understanding these state-specific legal requirements can help individuals and businesses determine their insurance bond needs. Furthermore, an experienced insurance agent can help you obtain an insurance bond.
Insurance Bonds with Torian Insurance
Torian Insurance is well-versed in providing comprehensive insurance bond services from surety bonds to fidelity bonds. With a deep understanding of the nuances of bonds, the team at Torian Insurance is able to cater to the specific needs of individuals, families, and businesses and offer the best rates they can find from their pool of resources.
Choosing Torian Insurance for insurance bonds comes with significant benefits. Clients can expect a personalized approach, where their needs and circumstances are thoroughly assessed to provide the most appropriate bond. Moreover, Torian Insurance prides itself on its excellent customer service, ensuring that clients have a seamless and stress-free experience.
Secure Your Business with the Right Business Insurance Coverage
As we’ve explored, insurance bonds are a critical component in navigating financial risks.
Torian Insurance, with its rich legacy and customer-centric approach, excels in providing personalized business insurance solutions. Its team of experienced professionals is well-versed in all types of insurance bonds and adept at providing informed advice.
Are you considering an insurance bond? Let us guide you through the process and help you make the best decision for your situation.
Reach out to Torian Insurance today and experience the peace of mind that comes with knowing you are well protected.



